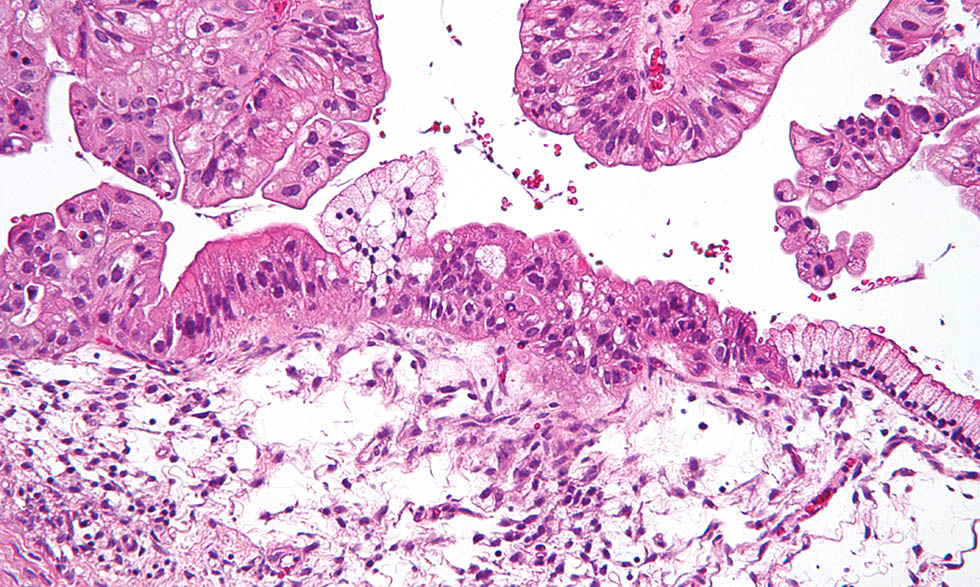
All ovarian cancers involve one or both ovaries, or in the nearby tissue that covers organs in the abdomen (belly area). There are three types of ovarian cancers: epithelial ovarian carcinomas, germ cell tumors, and stromal cell tumors. Each has different characteristics and traits:
Epithelial ovarian carcinomas: These are the most common type of ovarian cancer. About 85% to 90% of these cancers involve the cells that cover the outer surface of the ovary. They commonly spread first to the lining and organs of the pelvis and abdomen and then to other parts of the body. Nearly 70% of women with this type of ovarian cancer are diagnosed in the advanced stages.
Germ cell tumors: These make up less than 2% of all ovarian cancers. They begin in the reproductive cells that are a woman's "eggs". Ninety percent of patients with germ cell tumors survive five years after diagnosis. Teenagers and women in their 20s are more likely to develop this type of ovarian cancer.
Stromal cell tumors: These represent about 1% of all ovarian cancers. They form in the tissues that support the ovaries. This type of cancer is often found in the early stages. Vaginal bleeding is one of the most common